In the part one post on this subject we mentioned that the allure posed by less stringent regulations in Satellite Accumulation Areas (SAAs) can be problematic for generators who might misclassify their accumulation areas as SAAs instead of the more regulated 90-day areas. Since this is a violation of EPA regulations it is imperative that generators know not only the difference between the two storage area types but also what must be done at each.
What is the difference between an SAA and a 90-Day?
A 90-day storage area is different from an SAA because it is an area where wastes can be stored for less than 90 days without a permit. An SAA has no strict time limit associated with it, just a quantity limit. Additionally, the time clock for wastes stored in an SAA does not start until the waste is moved to the waste storage area, in this case a 90-day. So the two differences between SAAs and 90-days is the amount of waste that can be stored and the length of time it can be stored before needing to be treated or shipped offsite for management.
How should containers be managed in a 90-Day?
As stated by the EPA, “The moment that waste is placed in the container, containers holding hazardous waste must be managed to prevent spills of hazardous waste.” The best way to prevent spills is by making sure that your containers are in good condition before, during, and after waste is placed in them. Containers in good condition should be free of dents and corrosion (which weaken the container), free of leaks, structurally sound, and devoid of bulges.
According to §265.171, “If a container holding hazardous waste is not in good condition, or if it begins to leak, the owner or operator must transfer the hazardous waste from this container to a container that is in good condition, or manage the waste in some other way that complies with the requirements of this part.”
What if the containers in the 90-Day are already filled?
Companies that generate and store hazardous waste should have written procedures in place detailing how containers should be managed. Additionally, all employees should be trained in the procedures. At minimum the EPA requires that generators:
- Keep containers closed at all times, except when…adding or removing waste from the container;
- Be careful when…handling the containers. [Generators] must open, handle, and store containers to prevent ruptures or leaks. For example, use drum grapplers to lift and move drums — don’t hand-roll the drums from one area to another; and
- [Take note] if the container begins to leak, or you notice dents or bulges, [if this happens] transfer the waste to another container.
In addition to all of this, generators must also prevent reactions of ignitable and/or incompatible wastes. We will cover this topic in an upcoming blog post.
Quoted and cited information for this blog post (unless otherwise noted) was gathered from the EPA Handbook for Hazardous Waste Containers. As always, this blog post is not intended to be comprehensive and it is always best to check with the EPA and local government for full, up-to-date, rules and regulations.
More News From Heritage
-
Published Articles 8/2/22
How Safety, Maintenance, and Reliability Are Intertwined
VP of Health and Safety Jim Mangas discusses the importance of plant safety, maintenance, and reliability (featured in BIC Magazine July/Aug '22)
-
Blogs 7/28/22
Spotlighting Our Environmental Interns
Highlighting some of the wonderful interns we have at Heritage this year!
-
Blogs 7/11/22
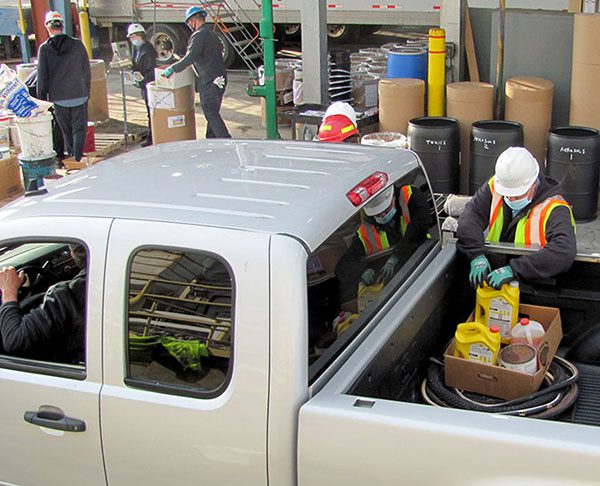
Turning Hazardous Waste into an Alternative Fuel
In this blog we walk you through the process of fuel blending, where we can turn hazardous waste materials into a viable alternative fuel source.
-
Community News 6/15/22
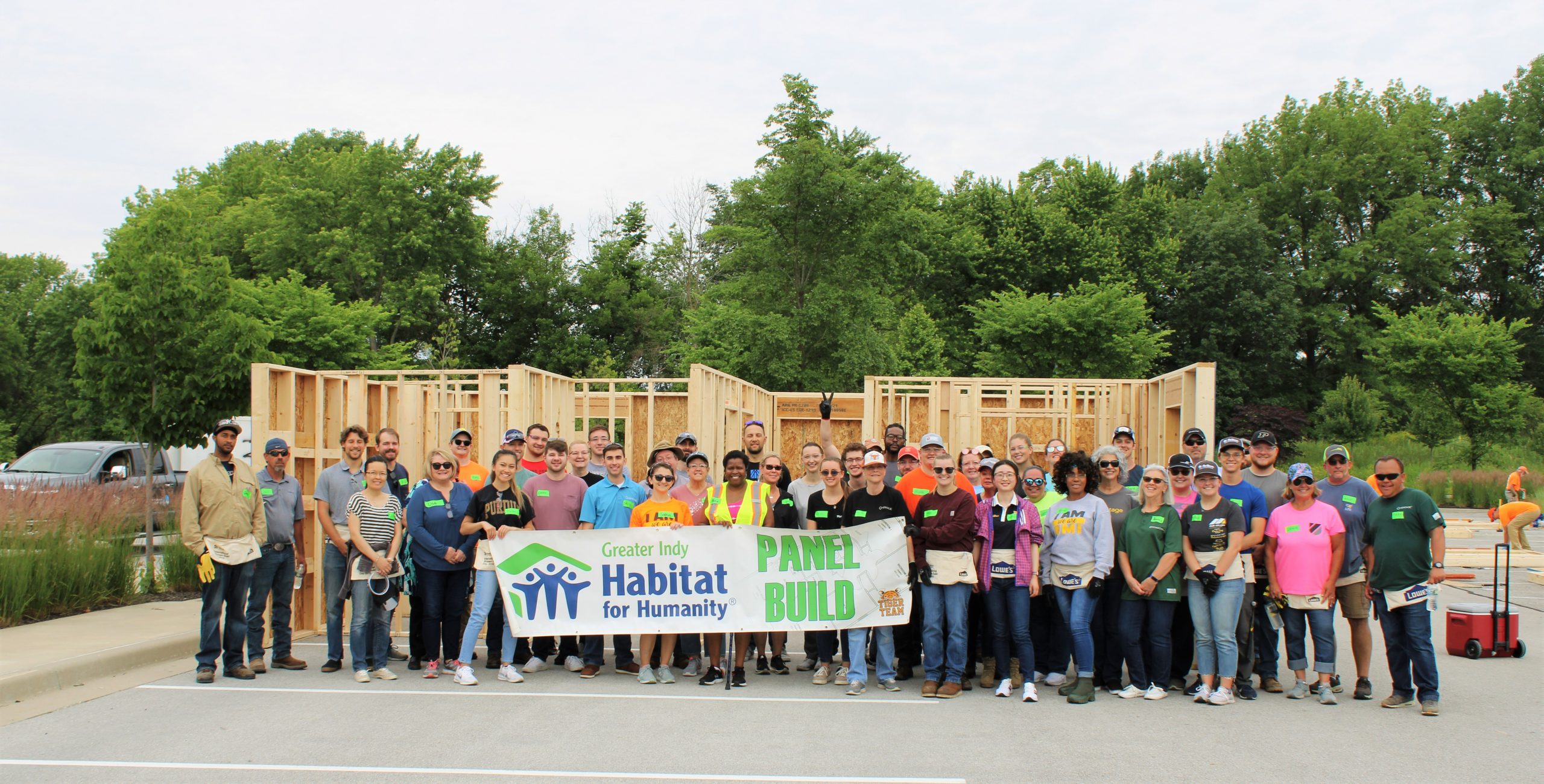
2022 Habitat for Humanity Build
Our 12th annual Habitat for Humanity Build
-
Blogs 4/13/22
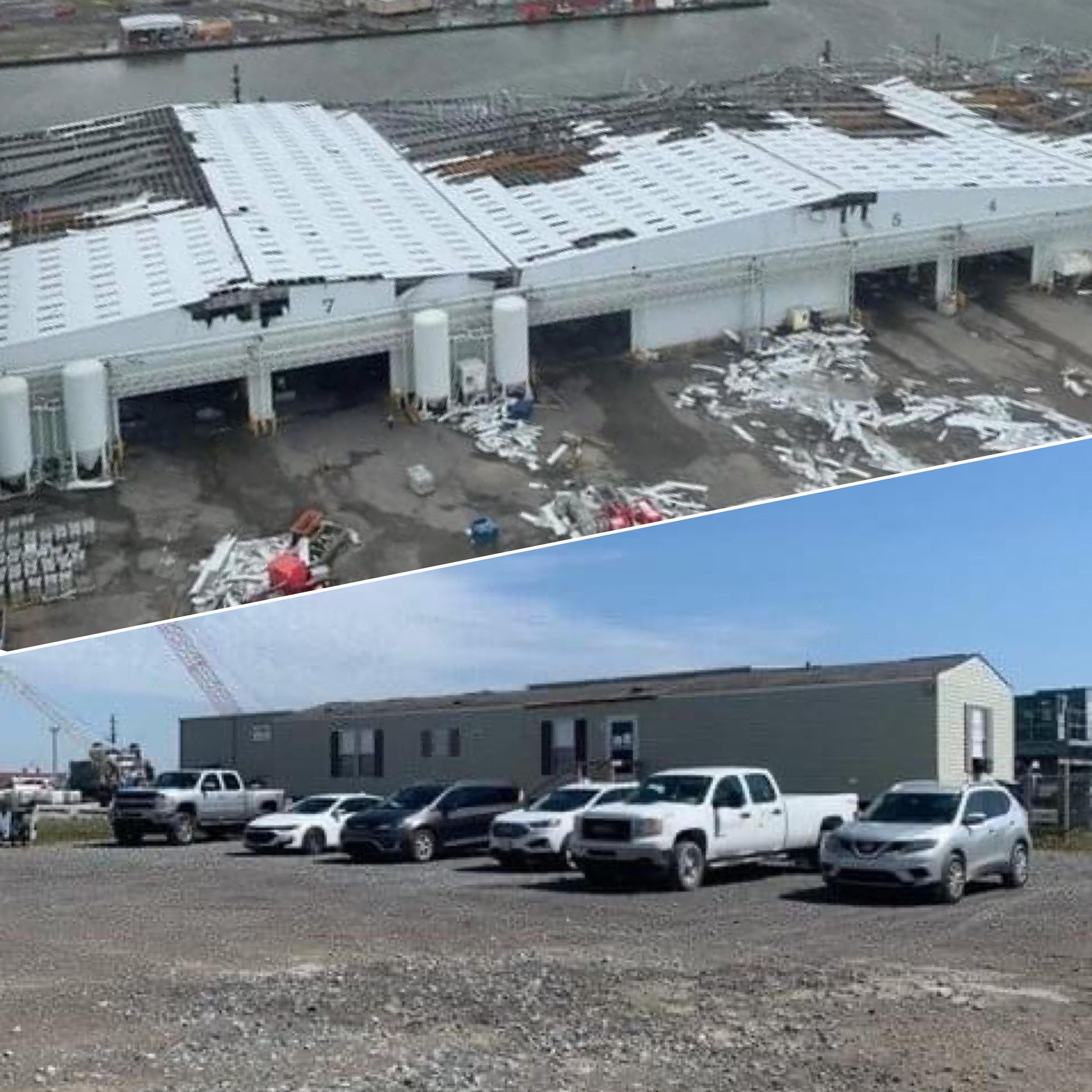
After Hurricane Ida, Our Port Fourchon Office Rebuilds
On August 28th, 2021, the Louisiana coast was battered by Hurricane Ida. This included our Port Fourchon Service Center, where the devastating hurrica
-
Community News 4/7/22
Heritage readies for Earth Day HHW collection in East Liverpool
Heritage Thermal Services is pleased to announce that its collection of household hazardous wastes for the East Liverpool area returns for 2022.
-
Published Articles 4/2/22
The Impact of Changing Conditions
VP of Health and Safety Jim Mangas discusses preparedness for unexpected conditions during a project. (featured in BIC Magazine March/April '22)
-
Blogs 3/11/22
International Women’s Week Spotlight – Rachel McGrogan
Rachel McGrogan speaks about her time as a Lab Chemist at Heritage.